Evisions Application Launcher
The Evisions Application Launcher is the program that launches the MAPS applications from the eLauncher and controls how the client applications connect to MAPS. When the user selects an application, the Evisions Application Launcher checks to see if there are multiple versions of the application available to the user; if so, it prompts the user to select a version.
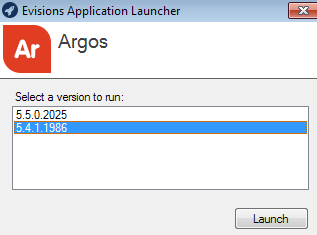
The Evisions Application Launcher also handles the connection between the application executable on the client's machine and the corresponding mapplet running on the server where MAPS is installed.
Installation
The Evisions Application Launcher (EAL) must be installed on each user's machine. For users who are able to install software on their computer, they will be prompted to download and install the EAL when attempting to launch any MAPS application for the first time after the new launcher has been enabled. They will also see this prompt whenever a MAPS update includes a new version of the EAL.
Users must have the Microsoft .NET Framework installed on their machines, or they will be prompted to install it while installing the EAL. Windows XP users require the Microsoft .NET Framework version 4.0. Users on later versions of Windows require version 4.5 or higher.
For institutions where end users do not have installation permissions for the machines they use to launch the applications, we have provided an .msi installer that your IT department can use to roll out the new launcher via Group Policy. Once you have upgraded MAPS to version 4.5, you can find the evisions_application_launcher.msi file on the machine where MAPS is installed. It will be located in the MAPS Service directory under \http_files\evisions_application_launcher. The full path will look similar to:
C:\Evisions\MAPS\Service\http_files\evisions_application_launcher\evisions_application_launcher.msi.
Your IT department should ensure that the Microsoft .NET Framework (version 4.0 for XP users, version 4.5 or higher for all Windows versions above XP) is installed on each machine where the Evisions Application Launcher will be installed.
MAPS Configuration
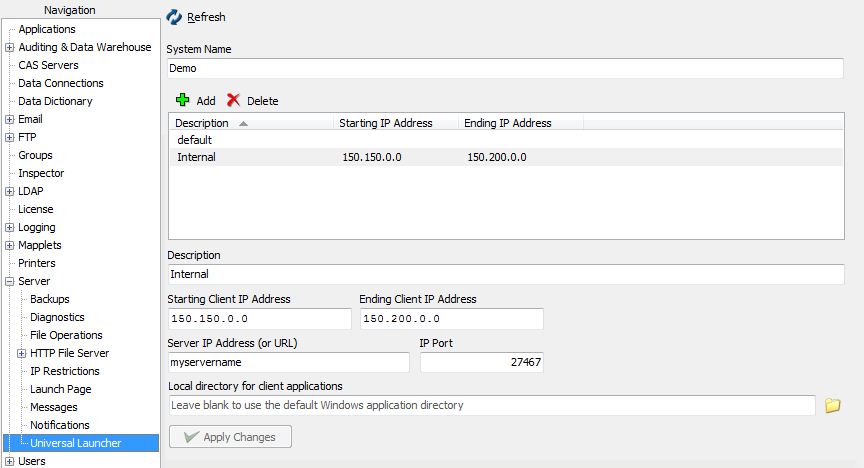
To configure options for the Evisions Application Launcher, go to Server -> Universal Launcher in the MAPS config.
Previous versions of MAPS provided two different versions of the launcher. The default prior to version 5.0 was a Java-based launcher which required users to have Java installed in their browser. This version was removed in MAPS 6.0, since most major browsers have dropped support for Java due to its inherent security risks.
System Name - The friendly name of this MAPS server. You can choose any name you like, though it should be identifiable to users. The system name appears at the bottom of the application windows and in connection dialogs, and is visible to end users.
IP ranges - You can control how different IP ranges access MAPS. For example, you may wish to use the server name to access MAPS internally, but wish to use your institution's URL to access it from the outside. Click the green Add button to add a new IP range.
Description - Enter a name to help you identify this IP range.
Starting/Ending Client IP Address - The starting and ending IP addresses that defines this range.
Server IP Address (or URL) - You can enter the server name for internal ranges, or an IP address or URL for external or external/internal access. The address specified must be visible to users in the IP range entered above.
Note: For clustered installations, the Server IP Address (or URL) should be populated by the URL of your load balancer, or load balancing software.
Port - The default MAPS port, as defined previously on the Server page.
Local directory for client applications - When a user accesses a MAPS application, the Evisions Application Launcher downloads the application executable to their local machine. By default, the applications are stored in:
Windows XP:
C:\Documents and Settings\[USERNAME]\Application Data\Evisions\MAPClients\Windows 7:
C:\Users\[USERNAME]\AppData\Roaming\Evisions\MAPClients\
You can change this directory to a location of your choosing. Keep in mind that MAPS creates this folder (in either the default or specified location) on every user's local machine.